Hydrophobic Investigation of Excimer Laser Effects on Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate)
Physics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14331/ijfps.2016.330095Keywords:
ArF laser, Hydrophobic, Laser ablation, Poly ethylene terephthalateAbstract
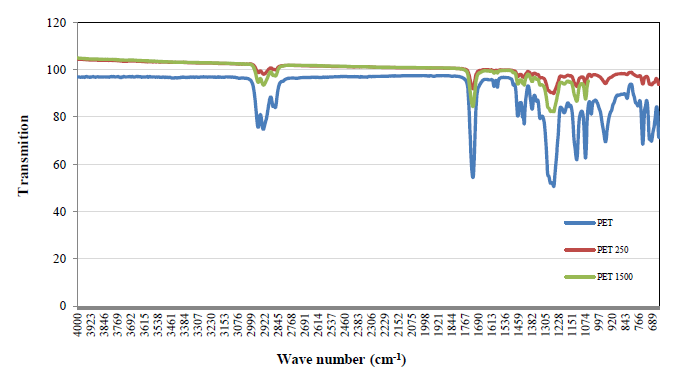
The modification on the surface of the polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymer as a result of ArF (193nm) laser irradiation was investigated. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy was employed for the examination of the chemical composition of irradiated surface and conical structure. FTIR spectroscopy indicates that by irradiation of PET, hydrophobic groups of the polymer molecules in the polymer chain have more freedom of movement and prevent the interaction between water molecules and the hydrophilic groups on the polymer surface, and PET surfaces after exposure have become more hydrophobic. While the PET is irradiated by more than 800 pulses, its surfaces become hydrophilic, so that the surface of PET after treated by 1500 pulses, even becomes more hydrophilic than that of untreated one.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 International Journal of Fundamental Physical Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










